Arithmetic operators are an essential component of any programming language, including PHP. They allow you to perform mathematical operations on numeric values, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and more. In PHP, you can use a variety of arithmetic operators to manipulate numeric data and perform calculations within your programs. Let’s explore the different arithmetic operators available in PHP.’
- Addition (+): The addition operator (+) is used to add two or more numeric values together. For example:
$x = 5;
$y = 10;
$sum = $x + $y;
echo $sum; // Output: 15
- Subtraction (-): The subtraction operator (-) is used to subtract one numeric value from another. For example:
$x = 15; $y = 7; $difference = $x - $y; echo $difference; // Output: 8
- Multiplication (): The multiplication operator () is used to multiply two or more numeric values together. For example:
$x = 4; $y = 6; $product = $x * $y; echo $product; // Output: 24
- Division (/): The division operator (/) is used to divide one numeric value by another. For example:
$x = 20; $y = 4; $quotient = $x / $y; echo $quotient; // Output: 5
- Modulo (%): The modulo operator (%) returns the remainder when one numeric value is divided by another. For example:
$x = 15;
$y = 7;
$remainder = $x % $y;
echo $remainder; // Output: 1
- Exponentiation (): The exponentiation operator () raises a numeric value to the power of another. For example:
$x = 2; $y = 3; $result = $x ** $y; echo $result; // Output: 8
These are the basic arithmetic operators in PHP. They can be combined and used within expressions to perform complex calculations. It’s important to keep in mind the operator precedence and use parentheses when necessary to control the order of operations.
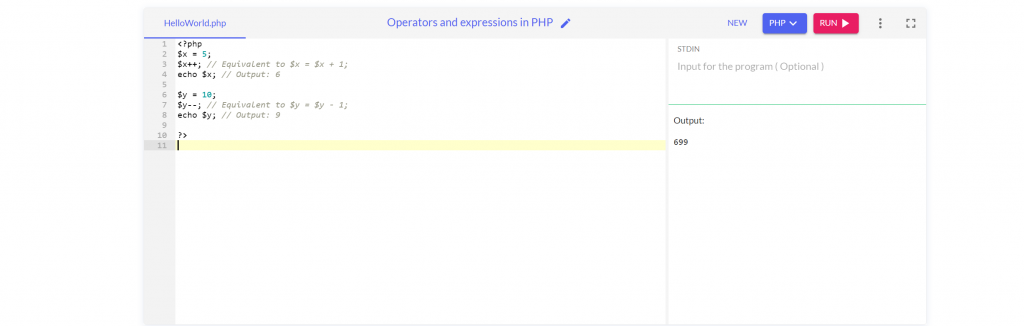
Additionally, PHP also provides increment (++) and decrement (–) operators, which are used to increase or decrease the value of a variable by one. Here’s an example:
$x = 5;
$x++; // Equivalent to $x = $x + 1;
echo $x; // Output: 6
$y = 10;
$y--; // Equivalent to $y = $y - 1;
echo $y; // Output: 9
These operators can be useful when working with loops or counting operations.
In conclusion, arithmetic operators in PHP provide the means to perform mathematical calculations and manipulate numeric data within your programs. By leveraging these operators, you can create dynamic and interactive PHP applications that handle numerical computations efficiently.
Assignment Operators in PHP
Assignment operators in PHP are used to assign values to variables. They provide a concise and efficient way to update the value of a variable based on arithmetic or logical operations. PHP offers several assignment operators that combine the assignment operation with another operation. Let’s explore the different assignment operators available in PHP.
- Assignment (=): The assignment operator (=) is the most basic assignment operator in PHP. It assigns the value on the right-hand side to the variable on the left-hand side. For example:
$x = 5; $y = $x; echo $y; // Output: 5
- Addition assignment (+=): The addition assignment operator (+=) adds the value on the right-hand side to the variable on the left-hand side and assigns the result to the variable. For example:
$x = 10; $x += 5; echo $x; // Output: 15
- Subtraction assignment (-=): The subtraction assignment operator (-=) subtracts the value on the right-hand side from the variable on the left-hand side and assigns the result to the variable. For example:
$x = 20; $x -= 7; echo $x; // Output: 13
- Multiplication assignment (=): The multiplication assignment operator (=) multiplies the variable on the left-hand side by the value on the right-hand side and assigns the result to the variable. For example:
$x = 4; $x *= 3; echo $x; // Output: 12
- Division assignment (/=): The division assignment operator (/=) divides the variable on the left-hand side by the value on the right-hand side and assigns the result to the variable. For example:
$x = 15; $x /= 5; echo $x; // Output: 3
- Modulo assignment (%=): The modulo assignment operator (%=) calculates the remainder when dividing the variable on the left-hand side by the value on the right-hand side and assigns the result to the variable. For example:
$x = 17; $x %= 5; echo $x; // Output: 2
- Concatenation assignment (.=): The concatenation assignment operator (.=) appends the value on the right-hand side to the string variable on the left-hand side. For example:
$str = "Hello"; $str .= " World!"; echo $str; // Output: Hello World!
These assignment operators allow you to update variables efficiently by combining assignment with arithmetic or string operations. They are particularly useful in scenarios where you need to perform calculations or concatenate strings and store the result back into a variable.
It’s important to note that assignment operators follow the right-to-left associativity, meaning that the operation is performed from right to left. For example, in the expression $x += $y += $z, the addition operation between $y and $z is performed first, and then the result is added to $x.
By leveraging assignment operators, you can write concise and readable PHP code while efficiently managing variable values and performing operations on them.
Comparison Operators in PHP
Comparison operators in PHP are used to compare two values and determine the relationship between them. These operators evaluate expressions and return a Boolean value (true or false) based on the comparison result. PHP provides a set of comparison operators that allow you to perform different types of comparisons. Let’s explore the comparison operators available in PHP.
- Equal (==): The equal operator (==) checks if two values are equal, regardless of their data types. For example:
$x = 5;
$y = "5";
$result = ($x == $y);
echo $result; // Output: 1 (true)
- Identical (===): The identical operator (===) checks if two values are equal and of the same data type. For example:
$x = 5; $y = "5"; $result = ($x === $y); echo $result; // Output: 0 (false)
- Not equal (!=): The not equal operator (!=) checks if two values are not equal. It returns true if the values are different, and false if they are equal. For example:
$x = 10; $y = 5; $result = ($x != $y); echo $result; // Output: 1 (true)
- Not identical (!==): The not identical operator (!==) checks if two values are not equal or not of the same data type. It returns true if either the values or the types are different, and false if they are equal. For example:
$x = 10; $y = "10"; $result = ($x !== $y); echo $result; // Output: 1 (true)
- Greater than (>): The greater than operator (>) checks if the left-hand side value is greater than the right-hand side value. For example:
$x = 15; $y = 10; $result = ($x > $y); echo $result; // Output: 1 (true)
- Less than (<): The less than operator (<) checks if the left-hand side value is less than the right-hand side value. For example:
$x = 5; $y = 10; $result = ($x < $y); echo $result; // Output: 1 (true)
- Greater than or equal to (>=): The greater than or equal to operator (>=) checks if the left-hand side value is greater than or equal to the right-hand side value. For example:
$x = 10; $y = 10; $result = ($x >= $y); echo $result; // Output: 1 (true)
- Less than or equal to (<=): The less than or equal to operator (<=) checks if the left-hand side value is less than or equal to the right-hand side value. For example:
$x = 5; $y = 10; $result = ($x <= $y); echo $result; // Output: 1 (true)
These comparison operators are useful for making decisions and controlling the flow of your PHP programs based on the relationship between values. They are commonly used in conditional statements (e.g., if, while) and logical expressions.
It’s important to note that the comparison operators do not modify the values being compared. They simply evaluate the expressions and return a Boolean result based on the comparison. Also, when comparing different data types, PHP performs type juggling to convert the values to a common type before making the comparison.
By utilizing comparison operators, you can perform various comparisons and make logical decisions in your PHP code based
Logical Operators in PHP
Logical operators in PHP are used to combine and manipulate logical conditions. These operators allow you to perform logical operations on Boolean values or expressions and determine the overall truth value. PHP provides three main logical operators: AND, OR, and NOT. Let’s explore each of these operators in detail.
- AND (&&): The AND operator (&&) returns true if both the left-hand side and the right-hand side conditions are true. If either of the conditions is false, it returns false. For example:
$x = 5;
$y = 10;
$result = ($x < 10 && $y > 5);
echo $result; // Output: 1 (true)
- OR (||): The OR operator (||) returns true if either the left-hand side condition or the right-hand side condition is true. It returns false only if both conditions are false. For example:
$x = 5; $y = 10; $result = ($x < 10 || $y < 5); echo $result; // Output: 1 (true)
- NOT (!): The NOT operator (!) is a unary operator that negates the truth value of a condition. It returns true if the condition is false and vice versa. For example:
$x = 5; $result = !($x == 5); echo $result; // Output: 0 (false)
Logical operators can also be combined to create more complex logical expressions. The precedence of the logical operators is as follows: NOT (!) has the highest precedence, followed by AND (&&), and then OR (||). Parentheses can be used to group conditions and control the order of evaluation.
Here’s an example that demonstrates the combination of logical operators:
$x = 5;
$y = 10;
$z = 3;
$result = ($x < 10 && $y > 5) || $z == 3;
echo $result; // Output: 1 (true)
In this example, the expression ($x < 10 && $y > 5) evaluates to true because both conditions are true. The expression $z == 3 also evaluates to true. Finally, the OR operator combines these two conditions, resulting in a true value.
Logical operators are commonly used in conditional statements (e.g., if, while) to control the flow of execution based on the truth value of conditions. They allow you to create complex conditions by combining multiple logical expressions.
It’s important to note that logical operators short-circuit the evaluation. This means that if the outcome of the expression can be determined by evaluating the left-hand side condition only, the right-hand side condition is not evaluated. This behavior can improve performance and prevent unnecessary evaluations.
By leveraging logical operators, you can create dynamic and flexible PHP code that handles different scenarios and makes decisions based on logical conditions.
String Operators and Expressions
String operators and expressions in PHP allow you to manipulate and concatenate strings, which are sequences of characters. PHP provides various operators and functions to perform operations on strings efficiently. Let’s explore the string operators and expressions available in PHP.
Concatenation operator (.) : The concatenation operator (.) is used to concatenate two or more strings together. It creates a new string by joining the operands. For example:
$string1 = "Hello";
$string2 = "World";
$result = $string1 . " " . $string2;
echo $result; // Output: Hello World
In this example, the concatenation operator (.) combines the strings $string1 and $string2 along with the space character, resulting in the string “Hello World”.
Concatenating assignment operator (.=) : The concatenating assignment operator (.=) is a shorthand notation for concatenation and assignment. It appends a string to an existing string variable. For example:
$name = "John";
$name .= " Doe";
echo $name; // Output: John Doe
In this example, the .= operator appends the string ” Doe” to the existing string stored in the variable $name.
String interpolation : PHP supports string interpolation, which allows you to embed variables directly within double-quoted strings. The variables are evaluated and replaced with their values within the string. For example:
$name = "Alice";
$message = "Hello, $name!";
echo $message; // Output: Hello, Alice!
In this example, the variable $name is interpolated within the double-quoted string, resulting in the output “Hello, Alice!”.
Escape sequences : PHP supports various escape sequences that allow you to include special characters within strings. Some commonly used escape sequences include:
\": Inserts a double quote within a double-quoted string.\': Inserts a single quote within a single-quoted string.\\: Inserts a backslash within a string.\n: Inserts a newline character.\r: Inserts a carriage return character.\t: Inserts a tab character.\xHH: Inserts a character based on its ASCII hexadecimal value (e.g.,\x41represents the letter “A”).
For example:
$message = "This is a \"quoted\" string.";
echo $message; // Output: This is a "quoted" string.
$quote = 'It\'s a beautiful day.';
echo $quote; // Output: It's a beautiful day.
These escape sequences allow you to include special characters and handle situations where quotes or other characters need to be included within strings.
In addition to these operators and expressions, PHP provides numerous string functions that allow you to manipulate strings in various ways. These functions include strlen(), substr(), str_replace(), strpos(), strtolower(), strtoupper(), and many more.
By leveraging string operators, expressions, and functions, you can manipulate and work with strings effectively in your PHP code. Whether it’s concatenating strings, interpolating variables, or applying string functions, PHP offers a rich set of tools for handling string data.
Increment/Decrement Operators
Increment and decrement operators in PHP are used to increase or decrease the value of a variable by one. These operators provide a convenient way to update the value of a variable in a concise manner. PHP offers two types of increment/decrement operators: pre-increment/decrement and post-increment/decrement. Let’s explore each of these operators in detail.
- Pre-increment (++$x) and Pre-decrement (–$x):
- The pre-increment operator (++$x) increments the value of the variable
$xby one and then returns the incremented value. - The pre-decrement operator (–$x) decrements the value of the variable
$xby one and then returns the decremented value.
- The pre-increment operator (++$x) increments the value of the variable
Example:
$x = 5;
echo ++$x; // Output: 6
echo --$x; // Output: 5
In the above example, the pre-increment operator ++$x increments the value of $x from 5 to 6 and returns the incremented value. Similarly, the pre-decrement operator --$x decreases the value of $x from 6 to 5 and returns the decremented value.
- Post-increment ($x++) and Post-decrement ($x–):
- The post-increment operator ($x++) increments the value of the variable
$xby one but returns the original value before the increment. - The post-decrement operator ($x–) decrements the value of the variable
$xby one but returns the original value before the decrement.
- The post-increment operator ($x++) increments the value of the variable
Example:
$x = 5;
echo $x++; // Output: 5
echo $x--; // Output: 6
In the above example, the post-increment operator $x++ returns the value of $x (5) and then increments it to 6. The post-decrement operator $x-- returns the value of $x (6) and then decrements it back to 5.
Increment and decrement operators are commonly used in loops and other scenarios where you need to iterate over values or adjust a variable’s value. They provide a concise way to update variables by a fixed amount.
It’s important to note that increment and decrement operators have side effects. If used within larger expressions, the order of evaluation may affect the outcome. To avoid confusion, it’s generally recommended to use increment and decrement operators in a standalone manner or within simple expressions.
By utilizing increment and decrement operators, you can easily modify the value of variables and perform iterative operations in your PHP code efficiently.
Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operators in PHP are used to perform operations on individual bits of integer values. These operators allow you to manipulate and extract specific bits within binary representations of numbers. PHP provides several bitwise operators that work on integer values. Let’s explore each of these operators in detail.
- Bitwise AND (&): The bitwise AND operator (&) performs a bitwise AND operation between the corresponding bits of two integers. It returns a new integer where each bit is set to 1 only if both corresponding bits are 1. For example:
$a = 10; // Binary: 1010
$b = 6; // Binary: 0110
$result = $a & $b;
echo $result; // Output: 2 (Binary: 0010)
In this example, the bitwise AND operator (&) performs the operation on the binary representations of 10 and 6, resulting in the value 2.
- Bitwise OR (|): The bitwise OR operator (|) performs a bitwise OR operation between the corresponding bits of two integers. It returns a new integer where each bit is set to 1 if at least one of the corresponding bits is 1. For example:
$a = 10; // Binary: 1010
$b = 6; // Binary: 0110
$result = $a | $b;
echo $result; // Output: 14 (Binary: 1110)
In this example, the bitwise OR operator (|) performs the operation on the binary representations of 10 and 6, resulting in the value 14.
- Bitwise XOR (^): The bitwise XOR operator (^) performs a bitwise exclusive OR operation between the corresponding bits of two integers. It returns a new integer where each bit is set to 1 only if exactly one of the corresponding bits is 1. For example:
$a = 10; // Binary: 1010
$b = 6; // Binary: 0110
$result = $a ^ $b;
echo $result; // Output: 12 (Binary: 1100)
In this example, the bitwise XOR operator (^) performs the operation on the binary representations of 10 and 6, resulting in the value 12.
- Bitwise NOT (): Performs a bitwise negation operation on an integer. It flips each bit, turning 0s into 1s and 1s into 0s. For example:
$a = 10; // Binary: 00000000000000000000000000001010
$result = ~$a;
echo $result; // Output: -11 (Binary: 11111111111111111111111111110101)
In this example, the bitwise NOT operator (~) negates each bit of the binary representation of 10, resulting in the value -11.
- Bitwise left shift (<<) and right shift (>>): The bitwise left shift (<<) and right shift (>>) operators shift the bits of an integer value to the left or right, respectively, by a specified number of positions. For example:
$a = 10; // Binary: 1010
$result = $a << 2;
echo $result; // Output: 40 (Binary: 101000)
$b = 10; // Binary: 1010
$result = $b >> 1;
echo $result; // Output: 5 (Binary: 101)
In the first example, the bitwise left shift (<<) operator shifts the bits of 10 two positions to the left, resulting in the value 40. In the second example, the bitwise right shift (>>) operator shifts the bits of 10 one position to the right, resulting in the value 5.
Bitwise operators are primarily used in low-level programming, cryptography, and certain optimization scenarios where direct bit manipulation is required. They can also be useful for handling and extracting specific flags or bits within binary data.
By leveraging bitwise operators in PHP, you can perform bitwise operations on integer values, manipulate individual bits, and achieve fine-grained control over binary representations of numbers.
Conclusion
Operators and expressions play a crucial role in PHP programming, allowing developers to perform a wide range of operations on variables, values, and data structures. PHP offers a rich set of operators, including arithmetic, assignment, comparison, logical, string, increment/decrement, and bitwise operators, each serving specific purposes.
Arithmetic operators enable mathematical calculations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and modulus. Assignment operators allow for assigning values and performing operations simultaneously, making code concise and efficient. Comparison operators are used to compare values and determine equality or inequality.
Logical operators enable the manipulation of Boolean values and the creation of complex conditional expressions. String operators and expressions facilitate string concatenation, interpolation, and manipulation. Increment and decrement operators provide a convenient way to modify variables by incrementing or decrementing their values.
Additionally, PHP’s bitwise operators allow for manipulation of individual bits within integer values, enabling low-level operations and bitwise calculations.
Understanding and effectively using operators and expressions in PHP is essential for performing calculations, making decisions based on conditions, manipulating strings, and performing various other tasks in PHP programming. By utilizing these operators and expressions, developers can write concise, efficient, and expressive code.
It’s important to note that operators have precedence and associativity rules that determine the order in which operations are evaluated. Being aware of these rules and using parentheses when necessary ensures correct and expected results.
Overall, a strong understanding of operators and expressions empowers PHP developers to write powerful and efficient code, handling data and performing operations effectively in a wide range of scenarios.
Recent Comments