WordPress plugins are software components that extend the functionality of a WordPress website. They are written in PHP and can add new features, modify existing ones, or enhance the performance and security of the site. Plugins are designed to be easily installed and activated, allowing users to customize their websites without the need for coding or modifying the core WordPress files. With thousands of plugins available, their purpose is to empower users to tailor their WordPress sites to their specific needs, ranging from SEO optimization and contact forms to e-commerce solutions and social media integration.
Understanding Plugin Architecture
WordPress plugins are essential components that extend the functionality of a WordPress website. To effectively develop and work with plugins, it’s crucial to understand the underlying architecture of the WordPress plugin system. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements of WordPress plugin architecture:
- Plugin Files and Structure: WordPress plugins are typically organized into folders within the
wp-content/pluginsdirectory. Each plugin resides in its own folder, which contains one or more PHP files. The main plugin file, often namedplugin-name.php, acts as the entry point for the plugin and contains essential information and hooks to integrate with WordPress. - Plugin Header: The plugin header is a block of metadata located at the top of the main plugin file. It includes information such as the plugin name, description, version, author, and other details. This header is crucial for WordPress to recognize and manage the plugin.
- Hooks and Filters: WordPress relies on hooks and filters to allow plugins to interact with its core functionality. Hooks are specific points in the execution flow where plugin functions can be attached to perform actions or modify data. Filters, on the other hand, enable plugins to modify or filter content or data before it is displayed or saved.
- Plugin Activation and Deactivation: When a plugin is activated, WordPress executes the necessary code defined in the activation hook, allowing the plugin to perform initialization tasks, such as setting up database tables or adding default options. Similarly, deactivation hooks are triggered when a plugin is deactivated, providing an opportunity to clean up or remove any modifications made by the plugin.
- Plugin Settings and Options: Plugins can have settings and options that allow users to configure their behavior. These settings are typically stored in the WordPress database and can be accessed and modified through the WordPress Settings API. Plugins can add their own admin pages or integrate with existing ones to provide a user-friendly interface for managing settings.
- Plugin Security: As plugins can introduce vulnerabilities if not developed properly, it’s crucial to prioritize security when working with plugin architecture. Following best practices, such as validating user input, sanitizing and escaping data, and using secure coding practices, helps protect against common security threats.
Understanding the WordPress plugin architecture enables developers to create powerful and well-integrated plugins that seamlessly extend WordPress functionality. By leveraging hooks, filters, activation/deactivation processes, settings, and security considerations, developers can build robust plugins that enhance the user experience and add valuable features to WordPress websites.
Types of WordPress Plugins
WordPress offers a vast array of plugins that cater to different needs and functionalities. These plugins can be categorized into several types based on their purpose and the features they provide. Here are some common types of WordPress plugins:
- Utility Plugins: Utility plugins offer general-purpose functionality that enhances the overall performance and management of a WordPress site. They may include cache plugins for optimizing site speed, backup and restore plugins for data protection, security plugins for safeguarding against threats, and maintenance plugins for handling routine tasks.
- SEO Plugins: SEO plugins help optimize a website for search engines. They provide tools for meta tag management, XML sitemap generation, keyword analysis, and content optimization. SEO plugins can assist in improving website visibility, increasing organic traffic, and enhancing search engine rankings.
- Security Plugins: Security plugins focus on protecting WordPress sites from various security threats, such as malware, hacking attempts, and unauthorized access. They offer features like firewall protection, login security, file integrity monitoring, and security scanning to fortify the website’s defenses.
- E-commerce Plugins: E-commerce plugins transform a WordPress site into an online store. They enable features like product listings, shopping carts, secure payment gateways, inventory management, and order tracking. E-commerce plugins make it easier to sell products or services online and manage the entire sales process.
- Social Media Plugins: Social media plugins integrate social sharing and engagement features into a WordPress site. They allow visitors to share content on social platforms, display social media feeds, and provide options for following and connecting with the website owner on various social networks.
- Form Builder Plugins: Form builder plugins simplify the creation and management of contact forms, surveys, and other types of web forms. These plugins typically offer drag-and-drop interfaces, customization options, and integration with email marketing services, making it easy to collect user information and facilitate communication.
- Content Management Plugins: Content management plugins help organize and present content in various ways. They may include page builders for creating visually appealing layouts, gallery plugins for showcasing images and videos, and editorial calendar plugins for managing content publishing schedules.
- Membership and Subscription Plugins: Membership and subscription plugins enable the creation of membership-based websites, paid content access, and subscription models. They provide features like user registration, membership levels, access controls, and payment gateways, allowing site owners to monetize content and offer exclusive benefits to subscribers.
These are just a few examples of the types of WordPress plugins available. The WordPress plugin ecosystem is vast and diverse, offering plugins for nearly any functionality or customization need you may have for your website. When choosing plugins, consider the reputation, compatibility with your WordPress version, active support, and user reviews to ensure you select reliable and well-maintained options that suit your specific requirements.
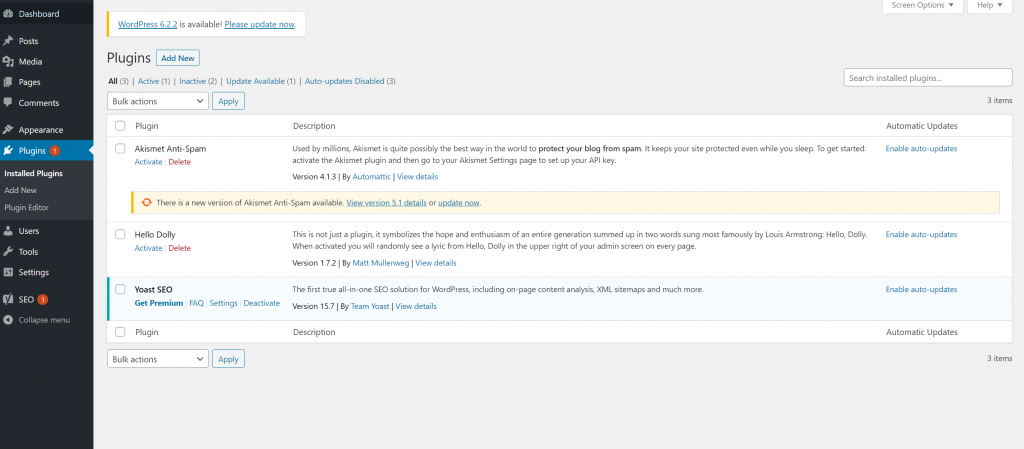
Installing and Managing Plugins
One of the key advantages of using WordPress is its extensive plugin ecosystem, which allows you to enhance your website’s functionality with ease. Installing and managing plugins in WordPress is a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Access the WordPress Admin Dashboard: Log in to your WordPress website and access the admin dashboard. The login URL is typically yourdomain.com/wp-admin.
- Navigate to the Plugins Menu: In the admin dashboard, locate the “Plugins” menu item in the sidebar. Hover over it, and you will see two options: “Installed Plugins” and “Add New.”
- Installing a Plugin: To install a plugin, click on “Add New” in the Plugins menu. You will be taken to the “Add Plugins” page. Here, you have multiple options: a. Search: Enter a keyword related to the plugin you want in the search bar. WordPress will display relevant plugins. Once you find the desired plugin, click “Install Now.” b. Upload: If you have a plugin in the form of a ZIP file, click on the “Upload Plugin” button, select the ZIP file from your computer, and click “Install Now.” c. Featured, Popular, or Recommended: WordPress provides curated lists of plugins under these sections. You can browse through them and click “Install Now” for any plugin you want to add.
- Activate the Plugin: After installing a plugin, you need to activate it for it to start working on your website. Once the installation is complete, click on the “Activate” button that appears. The plugin will then be activated and ready to use.
- Manage Installed Plugins: To manage your installed plugins, go to the “Installed Plugins” page under the Plugins menu. Here, you will see a list of all the plugins you have installed. From this page, you can: a. Activate/Deactivate: Activate or deactivate a plugin by clicking the corresponding links. b. Edit: Edit the plugin’s code directly from the admin dashboard, but exercise caution as this can potentially break functionality. c. Delete: Remove a plugin completely from your website by clicking the “Delete” link. Note that deleting a plugin will also delete its settings and data.
- Configure Plugin Settings: Some plugins have their own settings that can be configured. Usually, you can find these settings under a separate menu item created by the plugin, such as “Settings” or “Plugin Name” in the sidebar of the admin dashboard. Visit the plugin’s settings page to customize its functionality according to your needs.
- Update Plugins: Plugin updates are crucial for security, bug fixes, and compatibility with the latest WordPress version. When updates are available, you will see a notification in the admin dashboard and under the “Plugins” menu. To update a plugin, simply click on the “Update Now” link.
Installing and managing plugins in WordPress empowers you to customize your website and add new features without the need for extensive coding knowledge. However, it’s important to select reputable plugins from trusted sources, keep them updated, and regularly review your installed plugins to ensure they align with your website’s goals and maintain optimal performance.
Customizing Plugins
While WordPress plugins offer valuable functionality out of the box, sometimes you may need to customize them to better align with your specific needs and design preferences. Customizing plugins allows you to tailor their behavior, appearance, and integration within your website. Here are some ways to customize plugins in WordPress:
- Plugin Settings: Many plugins provide settings that allow you to customize their behavior. These settings can usually be found in a dedicated menu item created by the plugin in the WordPress admin dashboard. Explore the available settings and adjust them according to your requirements. Common options may include layout choices, color schemes, default values, or integration settings.
- Custom CSS: If you want to change the appearance of a plugin’s elements, such as adjusting font styles, margins, or colors, you can use custom CSS. WordPress provides options to add custom CSS code through the theme customizer or by using a plugin specifically designed for custom CSS. Write CSS rules that target the specific elements of the plugin and apply the desired styling.
- Template Overrides: Some plugins allow you to override their default templates to customize the way content is displayed. To do this, locate the plugin’s template files within the plugin’s folder. Create a folder named “plugin-name” in your theme directory and replicate the plugin’s file structure within it. Make necessary modifications to the templates in your theme folder, and WordPress will use these custom template files instead of the plugin’s default ones.
- Filters and Hooks: WordPress provides an extensive system of filters and hooks that allow you to modify the functionality of plugins without modifying their code directly. Plugins often expose hooks that you can leverage to add or remove functionality, modify data, or change the plugin’s behavior. You can add your own custom functions using WordPress’ add_filter() and add_action() functions to hook into the plugin’s actions and filters.
- Custom Plugin Development: If the desired customization goes beyond the options provided by the plugin or the ability to modify templates and hooks, you may need to consider custom plugin development. You can create a new plugin or extend an existing one to add the specific functionality or modifications you require. Custom plugin development requires coding knowledge and understanding of the WordPress Plugin API.
Note: When customizing plugins, it’s important to keep a few things in mind. First, always make a backup of your website before making any modifications to plugins to avoid potential issues or conflicts. Additionally, be mindful of plugin updates, as they may override your customizations. Document your customizations, and periodically review and test them after plugin updates to ensure they still work as intended.
Customizing plugins allows you to tailor their functionality and appearance to meet your specific requirements. By exploring available settings, leveraging custom CSS, overriding templates, utilizing filters and hooks, or even developing custom plugins, you can extend the capabilities of existing plugins and make them seamlessly integrate with your WordPress website.
Considerations for Choosing Plugins
WordPress plugins are an essential part of extending the functionality and features of your website. However, with thousands of plugins available, it’s important to make informed choices to ensure compatibility, reliability, and optimal performance. Here are some considerations to keep in mind when choosing plugins in WordPress:
- Purpose and Features: Clearly define the purpose and functionality you need from a plugin. Identify the specific features you require, whether it’s SEO optimization, e-commerce capabilities, form building, or social media integration. Focus on plugins that specialize in providing those features to avoid unnecessary bloat and conflicts.
- Reviews and Ratings: Before installing a plugin, check the reviews and ratings from other users. Look for plugins that have positive reviews, a high rating, and a significant number of installations. Reviews can provide insights into the plugin’s performance, reliability, ease of use, and customer support.
- Plugin Compatibility: Ensure that the plugin you choose is compatible with your version of WordPress. Plugins should clearly state their compatibility with the latest WordPress release. Outdated plugins may not work correctly or can cause conflicts and security vulnerabilities.
- Active Development and Support: Check if the plugin is actively developed and maintained by looking at the plugin’s documentation or website. Regular updates indicate that the developers are addressing bugs, security issues, and adding new features. Active support from the plugin developer, through forums or dedicated support channels, is also crucial if you encounter any issues or need assistance.
- Plugin Performance: A poorly optimized plugin can slow down your website and negatively impact user experience. Look for plugins that are lightweight and designed for efficiency. Plugins that have a positive reputation for performance and minimal impact on page loading times are preferable.
- Security and Reliability: Consider the security track record of a plugin and the reputation of its developer. Look for plugins that have been audited for security vulnerabilities or have a good security track record. Check if the developer responds promptly to security vulnerabilities and provides timely updates.
- Compatibility with Other Plugins and Themes: Plugins should not cause conflicts with other plugins or themes you have installed. Review user feedback to see if there are any reported conflicts or compatibility issues. Additionally, consider whether the plugin has built-in compatibility with popular themes or other plugins you are using.
- Documentation and User-Friendly Interface: Look for plugins that provide comprehensive documentation, tutorials, or user guides. A well-documented plugin makes it easier for you to understand its features, configuration options, and integration with your website. Additionally, a user-friendly interface and intuitive settings panel contribute to a smoother user experience.
- Regular Updates and Longevity: Plugins that receive regular updates demonstrate the developer’s commitment to improving and maintaining the plugin. This is particularly important for compatibility with new WordPress versions, bug fixes, and security patches. Avoid plugins that have not been updated for a long time, as they may not be compatible with the latest WordPress standards.
By considering these factors when choosing plugins, you can ensure that you select reliable, secure, and well-supported options that align with your website’s needs. It’s also recommended to keep the number of plugins to a minimum and regularly review and update them to maintain a healthy and optimized WordPress website.
Conclusion
Plugins play a crucial role in the WordPress ecosystem, offering a wide range of functionalities and features that enhance the core capabilities of a WordPress website.
In summary, plugins play a pivotal role in WordPress by extending functionality, providing customization options, saving time and costs, enabling accessibility for non-technical users, fostering community support, ensuring seamless integration, facilitating scalability, and embracing continuous improvement. Leveraging the power of plugins allows WordPress users to create dynamic, feature-rich websites tailored to their specific needs and goals.
Recent Comments